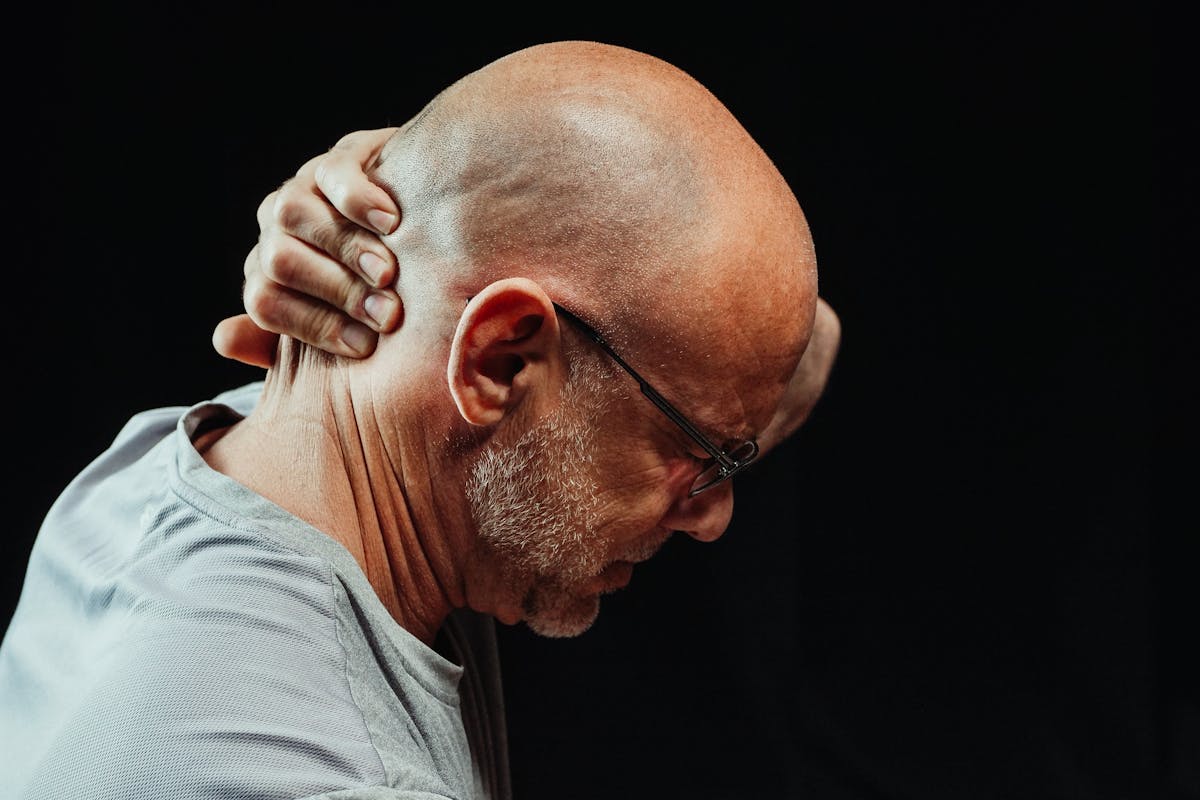
You know that pain that doesn’t go away and has been with you for weeks, months or even years? It is known as chronic pain, precisely because of its constancy.
In the rush of everyday life, routine, work and chores, pain ends up taking a back seat.
Therefore, it is common when the pain is not really strong or worrying, for the patient to postpone a consultation, tests and consequently the treatment.
The truth is that it has become common sense that living with pain is normal. But it is not!
On the contrary! Pain in a certain region is a response from the body or a warning that must be analyzed and taken seriously.
But when left untreated it can worsen and even affect quality of life.
That’s why in this article we will explain important points related to the subject such as:
– What is chronic pain?
– What are the main causes;
– Symptoms;
– Effective treatments for chronic pain;
What is chronic pain?
Chronic pain is a persistent disease that affects millions of people across the globe. There are several possible explanations for why it happens, and it could have different symptoms.
Unlike acute pain, which is temporary and usually resulting from recent illness or injury, chronic pain can last for weeks, months, or years.
What are the main causes of chronic pain?
Causes are varied and can be triggered by various physical, emotional, and environmental factors. Therefore, one must be aware of the signs and factors that are likely to interfere with the clinical picture.
The following are some of the most common reasons for chronic pain:
1. Previous Injuries: Physical trauma, such as car accidents or falls, can result in chronic pain, even after healing.
2. Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome are associated with chronic pain.
3. Changes in the Nervous System: Nerve damage or changes in the functioning of the central nervous system can lead to amplification of pain, resulting in sensations of chronic pain.
4. Body and Mind: Chronic stress, anxiety, depression and other psychosocial factors can contribute to chronic pain.
5. Lifestyle: Lifestyle directly affects the body. Lack of exercise, stretching and poor diet are harmful to health and can lead to clinical conditions that lead to disease, such as being overweight.
Symptoms of chronic pain:
Symptoms of chronic pain will differ tremendously from one individual to another and based on the established cause. As such, a proper diagnosis is necessary, by experts in the area as doctors to advise you on how best to treat it.
The primary symptom of chronic pain, as noted earlier, is a continuing or intermittent pain lasting over three months.
Standard medication and treatments are not as effective anymore. This symptom is often paired with touch sensitivity, i.e. the areas where the pain is occurring become more sensitive to touch or pressure.
Trained injuries or accidents can cause the muscles to stiffen, another symptom of chronic pain, especially when followed by a prolonged period of inactivity.
Chronic pain is characterized by psychosomatic problems such as anxiety and sadness. They are secondary results after long spells of pain, tiredness and failure to accomplish routine functions.
But as symptoms tend to be very diverse and always immediately related to the cause, one should keep a very keen eye on changes happening in your mind and body.
Effective treatments for chronic pain
There are several treatment options, from conventional to holistic.
However, it is important to know more before deciding.
The definition of the best treatment for your condition must be made by a specialist doctor, as he will analyze not only the symptoms, but also the primary cause.
Among the main treatments for chronic pain, we find:
1. Medication: Such as painkillers, anti-inflammatories, antidepressants, among others.
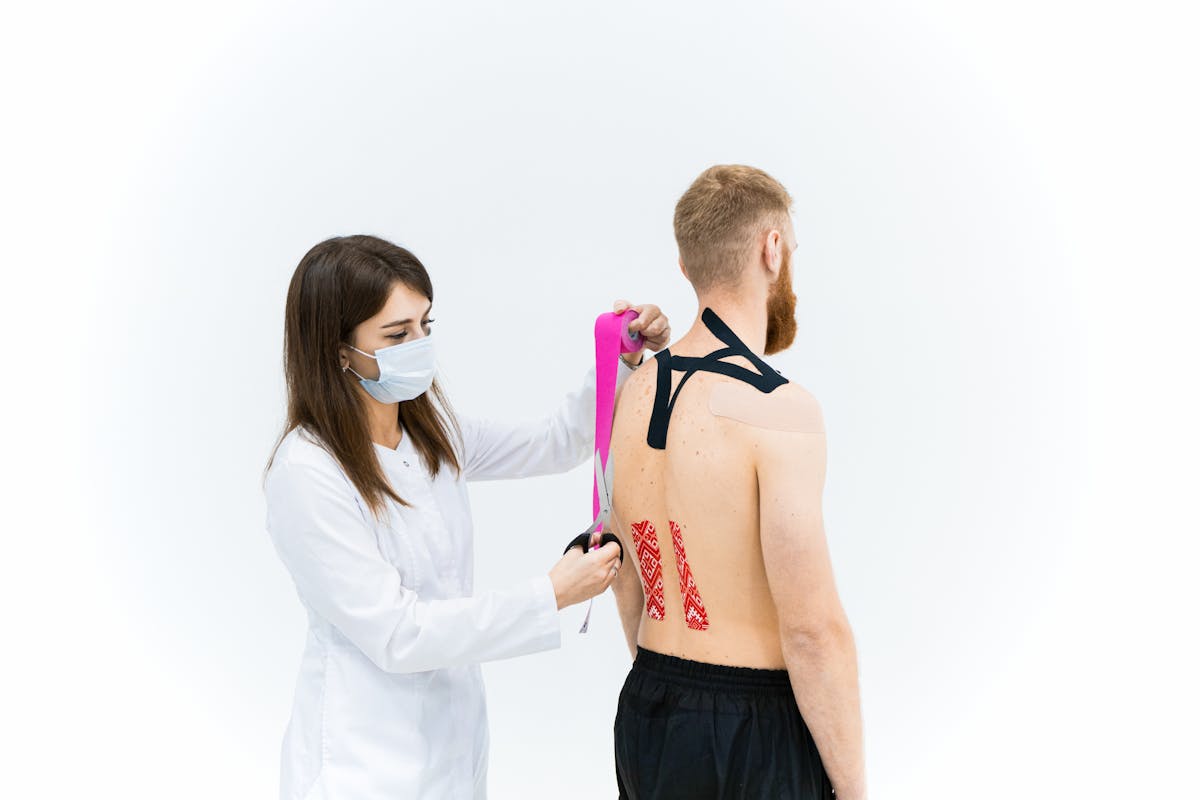
2. Physical Therapies: Physiotherapy, chiropractic, acupuncture and therapeutic massage.
3. Behavioral therapy: Monitoring with a psychologist or other professional who will control anxiety, depression and other causes.
4. Healthy lifestyle: Exercise, balanced diets, regular sleep, among others.
5. Minimally Invasive Treatments: Blockade for pain treatment. It can be used both in the prevention and treatment of chronic pain. Its purpose is to administer medication to a specific location, such as a nerve, muscle, tendon, subdermal, epidural, and to determine its action.


14 thoughts on “Chronic Pain: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments”
Comments are closed.